[ad_1]
When Meng Wanzhou returned home to China at the weekend, the presumed heiress of expertise group Huawei pledged to harness the teachings of just about three years in authorized limbo in Canada to the advantage of her firm.
“All of the frustration and difficulties, gratitude and emotion, steadfastness and accountability,” she informed a flag-waving welcome crowd on the tarmac at Shenzhen airport, “will rework into momentum for shifting us ahead, into braveness for our all-out struggle.”
Huawei will want all of the momentum and braveness it might probably muster.
By agreeing to a deferred fees deal over allegations of violating US sanctions towards Iran, Meng averted the specter of a prolonged jail sentence and closed a chapter that she stated had turned her life the other way up. However her firm expects to stay a goal of US prosecution and sanctions for years to return, and is barely simply determining how to do business under that pressure.

The US has banned using Huawei tools by the federal authorities, barred American corporations from promoting to Huawei with out an export licence, and prohibited the availability of any semiconductors designed or manufactured utilizing US expertise or tools to be used in any Huawei gear. That quantities to an nearly complete blockade of chip shipments to the Chinese language firm.
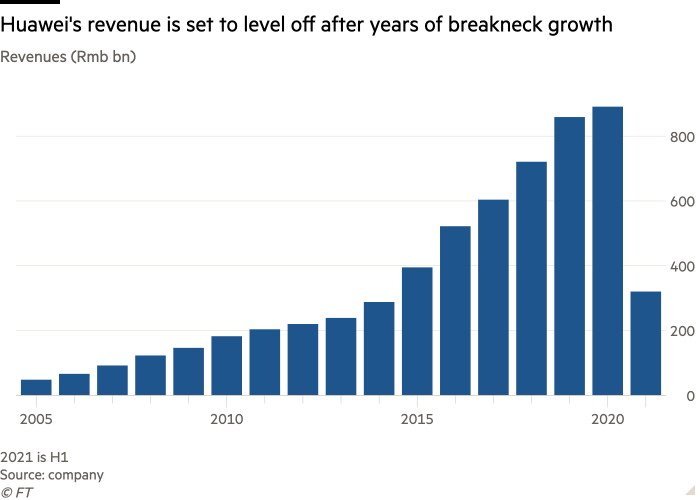
The affect on the group has been brutal. Within the first half of this yr, revenues fell by almost 30 per cent in contrast with the identical interval final yr, the most important ever drop.
Because the restrictions have begun to derail Huawei’s conventional enterprise, the group is now in a scramble to attempt to reinvent itself. The corporate is popping away from the event and sale of telecommunications community gear and smartphones into areas much less dependent on foreign chip supplies — corresponding to cloud companies and software program for good automobiles.
The group can be doubling down by itself analysis and improvement in a bid to flee the stranglehold of American sanctions. It’s investing closely to be a frontrunner within the rising 6G expertise so that other companies are dependent on its patents — relatively than Huawei counting on expertise imports from the US.
“Within the present local weather, the easiest way to explain the ambiance inside Huawei and the way in which we go about issues, is sort of a enormous assortment of start-ups,” says Henk Koopmans, the corporate’s head of analysis and improvement within the UK.
At stake isn’t just the destiny of one in every of China’s most distinguished and profitable corporations, however the broader technological competitors between Beijing and Washington. Chinese language officers are clear that Huawei has been an important a part of the nation’s community of innovation.
“Many have seen Huawei as the one risk for China to make a breakthrough in semiconductors and telecoms,” says a neighborhood authorities official in Shenzhen, the expertise business hub in southern China that’s Huawei’s house. “So Huawei should survive. It’s a nationwide mission.”
Part bottlenecks
The sanctions on Huawei have had a stark affect on each of its major companies — smartphones and telecoms infrastructure.
Its smartphone gross sales dropped by greater than 47 per cent within the first half of this yr in contrast with the identical interval final yr. Final week, rotating chair Eric Xu predicted that within the full yr, the corporate will lose as much as $40bn of its $50bn smartphone enterprise, a slide that analysts estimate will drive the share of the patron enterprise in Huawei’s complete revenues from 42 per cent earlier this yr to only over 30 per cent.
“Huawei’s element bottlenecks are actually beginning to chew,” says Ben Stanton, a smartphone analyst at analysis group Canalys. “Stockpiles are working low, and its quantity will nearly actually proceed to fall every quarter.” Noting that Huawei’s smartphone arm has retreated to its Chinese language house market, he provides that its power in earlier abroad strongholds corresponding to Europe “has fully evaporated”.
Within the community gear enterprise, the decline is going on extra slowly, partly as a result of product cycles are longer.
Dell’Oro, a telecom-focused analysis agency, stated in a observe earlier this yr that though Huawei can not procure customized application-specific chips for its telecom merchandise, it was assuring analysts that it had sufficient stock to maintain the infrastructure enterprise working within the close to time period.
In response to those losses, the primary massive push has been to strengthen Huawei’s software program capabilities in order that it’s much less depending on producing {hardware} that it’ll wrestle an increasing number of to ship with out entry to chip provides.
Xu informed reporters final week that whereas China was reaching encouraging ends in its efforts to develop its personal semiconductor business, it will take “a relatively very long time” till Huawei’s provide challenges could possibly be totally addressed.
The primary software-driven enterprise Huawei is dashing to construct is cloud services. A few of the features in a telecoms community historically carried out by base stations may be transferred to software program processes within the cloud with newer expertise. Furthermore, Huawei is quickly creating new cloud companies, which it affords to corporations and authorities departments. Final week, the corporate introduced plans to take a position $100m within the subsequent three years for small and medium-sized companies to develop on Huawei Cloud.

In response to Canalys, Huawei’s cloud enterprise grew by 116 per cent within the first quarter of this yr to take a 20 per cent share of a $6bn market in China, behind Alibaba Cloud however forward of Tencent. “Huawei Cloud’s outcomes have been boosted by web clients and authorities tasks, in addition to key wins within the automotive sector. It’s a rising a part of Huawei’s total enterprise,” says Matthew Ball, chief analyst at Canalys. He says that whereas roughly 90 per cent of this enterprise is in China, Huawei Cloud has a stronger presence in Latin America and Europe, Center East and Africa in contrast with Alibaba Cloud and Tencent Cloud.
There are limits on Huawei’s cloud enterprise, nonetheless. In July, Chinese language media reported that the corporate was contemplating promoting part of its server enterprise that runs on x86 central processing items after Intel’s export licence for offering Huawei with that element expired. Servers are indispensable for cloud corporations as a result of they’re the place the {hardware} knowledge is saved and far of the computing wanted for cloud companies is carried out. Huawei and Intel each declined to remark, however business specialists say processor provides are a headache for Huawei.
“Promoting the server enterprise is very doubtless,” says Ben Sheen, semiconductor analysis director for community and communication infrastructure at analysis agency IDC. “The CPU is a central element, and if Intel can not ship, Huawei is in massive hassle.”
As within the community gear enterprise, suppliers of cloud companies corresponding to Amazon Internet Companies or Google attempt to enhance efficiency by bettering their software program. If Huawei can obtain the identical, will probably be in much less pressing have to get new processor provides.
“In smartphones, your income share goes down in a short time for those who don’t have the newest chips. In cloud, you possibly can preserve working an honest enterprise for for much longer, and possibly even increase your income for those who put money into software program differentiation,” says Jue Wang, an affiliate associate within the expertise observe of Bain, a consulting firm.
Though corporations corresponding to Intel and AMD launch new CPUs yearly, the vast majority of cloud service suppliers’ servers run on processors two to 5 years outdated. The cloud corporations more and more generate new revenues by investing in new AI companies and instruments — even when their servers run on older chips. “However finally you have to new ones — you can’t provide cloud companies with out CPUs,” Wang says.
One of many fields the place Huawei finds it comparatively straightforward to choose up new enterprise helps to digitise industries which have been laggards within the adoption of data expertise. It’s providing telecom, IT and software program instruments to Chinese language corporations in sectors corresponding to coal mining and port operations, enabling them to decrease prices and improve safety. Pushed by these new operations, Huawei’s enterprise enterprise revenues grew by 23 per cent final yr and 18 per cent within the first half of this yr.
“The enterprise enterprise will doubtless proceed to be a development level for Huawei,” says Ethan Qi, an analyst at Counterpoint Analysis, who forecasts revenues in that phase to extend by as much as 15 per cent a yr within the subsequent few years.
Nonetheless, Huawei frets that this isn’t sufficient to offset the dying blow the US sanctions are dealing to the smartphone enterprise. The brand new business verticals “could not even be capable of compensate for these misplaced revenues in 10 years”, Xu informed reporters final week.

Gear change
Pissed off in its major markets, Huawei is making some placing bets on new areas. One of many largest is in electric and autonomous vehicles. Huawei made its first R&D foray into automobiles in 2014, however now the corporate is drastically cranking up dedication, with plans to type a 5,000-strong R&D group and funding of $1bn within the phase this yr.
The corporate says it is not going to construct automobiles itself, however its engineers are clearly wanting into every little thing wanting that. “Initially, we simply thought we might assist the automotive join, however after some time we realised that we will additionally assist make it extra clever,” says a Huawei official.
A automobile launched by Chinese language automaker Beiqi on the Shanghai Auto Present this yr featured a whole in-car electronics answer developed by Huawei. For this shift, the corporate is harnessing strengths constructed over years in its telecoms {hardware} enterprise — executives say expertise in designing base stations that may face up to excessive climate situations is useful as a result of temperature controls are a key requirement in electrical automobiles.
“They’ve refocused their groups within the analysis centres they run in Europe: Previously, these had been 3G and 4G-facing, and now they’re centered on [advanced driver-assistance systems],” says Jean-Christophe Eloy, chief government and president of Yole, a French expertise analysis and consultancy agency.
A big portion of the chips required in automotive electronics are manufactured with extra mature course of expertise, which doesn’t have to be imported. “A lot of that expertise is accessible in China,” Eloy stated. “Specializing in automotive due to this fact also can assist them get away from their chip provide downside.”

However Huawei has its sights set far past protecting the enterprise working within the close to time period: If something, its ambition to be a tech pioneer has grown even stronger. Ren Zhengfei, founder and chief government and Meng’s father, is letting a few of Huawei’s researchers off the leash to give attention to primary science and discover expertise breakthroughs even and not using a clear understanding of its potential enterprise functions.
“We is not going to demand you to place down your quill and be part of the troops,” Ren informed R&D workers at a gathering in August. He added that the analysis group at HiSilicon, Huawei’s chip design unit, could be saved although the US sanctions have robbed the Shenzhen-based operation of the possibility to fabricate its superior chips.
“We enable HiSilicon to proceed to scale the Himalayas,” Ren stated. “Nearly all of us others will keep down right here to develop potatoes, herd livestock and preserve sending provisions to the climbers, as a result of you possibly can’t develop rice on Mount Everest.”

‘Seize the patent entrance’
Final yr, Huawei invested Rmb141.9bn ($22bn) in R&D, nearly 16 per cent of its income.
The motive force behind this give attention to high-end analysis is the urge to turn into much less depending on international expertise — whereas additionally laying the groundwork for rising mental property royalties.
Already in 5G, Huawei is likely one of the most vital homeowners of patents, forcing rival community gear makers corresponding to Ericsson or Nokia to make sure funds to Huawei even when the Chinese language firm is excluded from 5G contracts in lots of western international locations.
Exhorting analysis workers to hunt international expertise management on the August assembly, Ren stated: “We analysis 6G as a precaution, to grab the patent entrance, to guarantee that when 6G in the future actually comes into use, we is not going to rely upon others.” Elaborating on the potential makes use of of 6G for the primary time, Ren stated the expertise would possibly, past telecom’s conventional realm of connectivity, be used for sensing and detection — features with potential to be used from healthcare to surveillance.
That expectation has grown out of the outcomes of the “assortment of start-ups” method touted by UK analysis head Koopmans. Ren’s encouragement for Huawei to pursue primary science is instilling what he hopes shall be a start-up mentality in most of the firm’s personal R&D workers.
As well as, it is usually tapping right into a rising variety of start-ups through which it invested in recent times. Engineers on the Centre for Built-in Photonics, a start-up primarily based in Ipswich, jap England, which Huawei acquired in 2012, not too long ago developed a laser on a chip that may direct mild right into a fibre-optic cable — an alternative choice to established telecoms expertise that sends pulses of infrared mild by means of the cable. The researchers constructed the chip themselves, utilizing Indium Phosphide expertise as a substitute of the mainstream silicon-based semiconductors the place US-owned software expertise provides Washington a stranglehold and which Huawei is struggling to acquire.

Koopmans says one future use of the expertise could possibly be transferring knowledge from sensors on the pores and skin measuring blood oxygen content material in distant healthcare companies. “And all this photonics exercise got here from a very researchy background the place we by no means knew if a product would ever see the sunshine of day. However that is how we’re doing issues now — reutilise our R&D capabilities in a non-monolithic manner.”
Ren will not be brief on ambition for the group’s R&D operations, however acknowledges that they may not present short-term outcomes.
“Some theories and papers might not be put to make use of till one or 200 years after they had been first printed,” he informed R&D workers, reminding them that the importance of Gregor Mendel’s genetics discoveries was not understood till a long time later. “Your paper could actually have a destiny like van Gogh’s work — no one confirmed curiosity in them for greater than 100 years, however now they’re priceless,” he stated. “Van Gogh starved.”
Extra reporting by Nian Liu in Beijing and Qianer Liu in Shenzhen
[ad_2]
Source

