[ad_1]
Scientists have recognized for many years that the particulate emissions from ships can have a dramatic impact on low-lying stratocumulus clouds above the ocean. In satellite tv for pc photos, components of the Earth’s oceans are streaked with vibrant white strips of clouds that correspond to delivery lanes. These artificially brightened clouds are a results of the tiny particles produced by the ships, and so they mirror extra daylight again to area than unperturbed clouds do, and way more than the darkish blue ocean beneath. Since these “ship tracks” block a few of the solar’s power from reaching Earth’s floor, they stop a few of the warming that will in any other case happen.
The formation of ship tracks is ruled by the identical fundamental rules behind all cloud formation. Clouds naturally seem when the relative humidity exceeds 100%, initiating condensation within the environment. Particular person cloud droplets type round microscopic particles referred to as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN). Usually talking, a rise in CCN will increase the variety of cloud droplets whereas decreasing their dimension. By a phenomenon generally known as the
Twomey effect, this excessive focus of droplets boosts the clouds’ reflectivity (additionally referred to as albedo). Sources of CCN embody aerosols like mud, pollen, soot, and even micro organism, together with man-made air pollution from factories and ships. Over distant components of the ocean, most CCN are of pure origin and embody sea salt from crashing ocean waves.
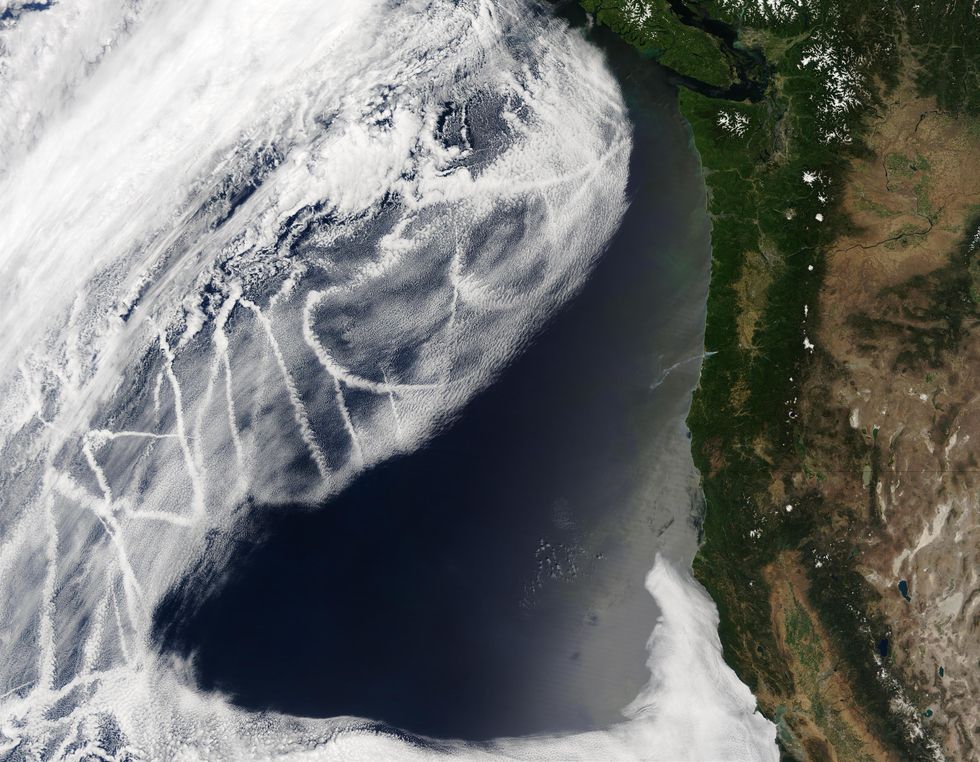

Satellite tv for pc imagery reveals “ship tracks” over the ocean: vibrant clouds that type due to particles spewed out by ships.Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Speedy Response Crew/GSFC/NASA
The intention of the MCB Mission is to think about whether or not intentionally including extra sea salt CCN to low marine clouds would cool the planet. The CCN could be generated by spraying seawater from ships. We anticipate that the sprayed seawater would immediately dry within the air and type tiny particles of salt, which might rise to the cloud layer by way of convection and act as seeds for cloud droplets. These generated particles could be a lot smaller than the particles from crashing waves, so there could be solely a small relative enhance in sea salt mass within the environment. The aim could be to supply clouds which are barely brighter (by 5 to 10 p.c) and presumably longer lasting than typical clouds, leading to extra daylight being mirrored again to area.
“Solar climate intervention“ is the umbrella time period for tasks comparable to ours that contain reflecting daylight to scale back international warming and its most harmful impacts. Different proposals embody sprinkling reflective silicate beads over polar ice sheets and injecting supplies with reflective properties, comparable to sulfates or calcium carbonate, into the stratosphere. Not one of the approaches on this younger subject are properly understood, and so they all carry doubtlessly massive unknown dangers.
Photo voltaic local weather intervention is
not a substitute for decreasing greenhouse gasoline emissions, which is crucial. However such reductions will not tackle warming from present greenhouse gases which are already within the environment. As the results of local weather change intensify and tipping factors are reached, we might have choices to forestall essentially the most catastrophic penalties to ecosystems and human life. And we’ll want a transparent understanding of each the efficacy and dangers of photo voltaic local weather intervention applied sciences so folks could make knowledgeable choices about whether or not to implement them.
Our group, primarily based on the
University of Washington, the Palo Alto Research Center (PARC), and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, contains specialists in local weather modeling, aerosol-cloud interactions, fluid dynamics, and spray techniques. We see a number of key benefits to marine cloud brightening over different proposed types of photo voltaic local weather intervention. Utilizing seawater to generate the particles provides us a free, ample supply of environmentally benign materials, most of which might be returned to the ocean by way of deposition. Additionally, MCB may very well be accomplished from sea degree and would not depend on plane, so prices and related emissions could be comparatively low.
The results of particles on clouds are momentary and localized, so experiments on MCB may very well be carried out over small areas and temporary time intervals (possibly spraying for just a few hours per day over a number of weeks or months) with out critically perturbing the atmosphere or international local weather. These small research would nonetheless yield important data on the impacts of brightening. What’s extra, we will rapidly halt using MCB, with very speedy cessation of its results.
Photo voltaic local weather intervention is the umbrella time period for tasks that contain reflecting daylight to scale back international warming and its most harmful impacts.
Our venture encompasses three vital areas of analysis. First, we have to discover out if we will reliably and predictably enhance reflectivity. To this finish, we’ll have to quantify how the addition of generated sea salt particles adjustments the variety of droplets in these clouds, and examine how clouds behave once they have extra droplets. Relying on atmospheric situations, MCB may have an effect on issues like cloud droplet evaporation charge, the chance of precipitation, and cloud lifetime. Quantifying such results would require each simulations and subject experiments.
Second, we’d like extra modeling to know how MCB would have an effect on climate and local weather each regionally and globally. Will probably be essential to check any adverse unintended penalties utilizing correct simulations earlier than anybody considers implementation. Our group is initially specializing in modeling how clouds reply to further CCN. Sooner or later we’ll should examine our work with small-scale subject research, which can in flip enhance the regional and international simulations we’ll run to know the potential impacts of MCB underneath totally different local weather change situations.
The third vital space of analysis is the event of a twig system that may produce the scale and focus of particles wanted for the primary small-scale subject experiments. We’ll clarify under how we’re tackling that problem.
One of many first steps in our venture was to establish the clouds most amenable to brightening. By modeling and observational research, we decided that the perfect goal is stratocumulus clouds, that are low altitude (round 1 to 2 km) and shallow; we’re significantly all in favour of “clear” stratocumulus, which have low numbers of CCN. The rise in cloud albedo with the addition of CCN is mostly sturdy in these clouds, whereas in deeper and extra extremely convective clouds different processes decide their brightness. Clouds over the ocean are typically clear stratocumulus clouds, which is lucky, as a result of brightening clouds over darkish surfaces, such because the ocean, will yield the best albedo change. They’re additionally conveniently near the liquid we wish to spray.
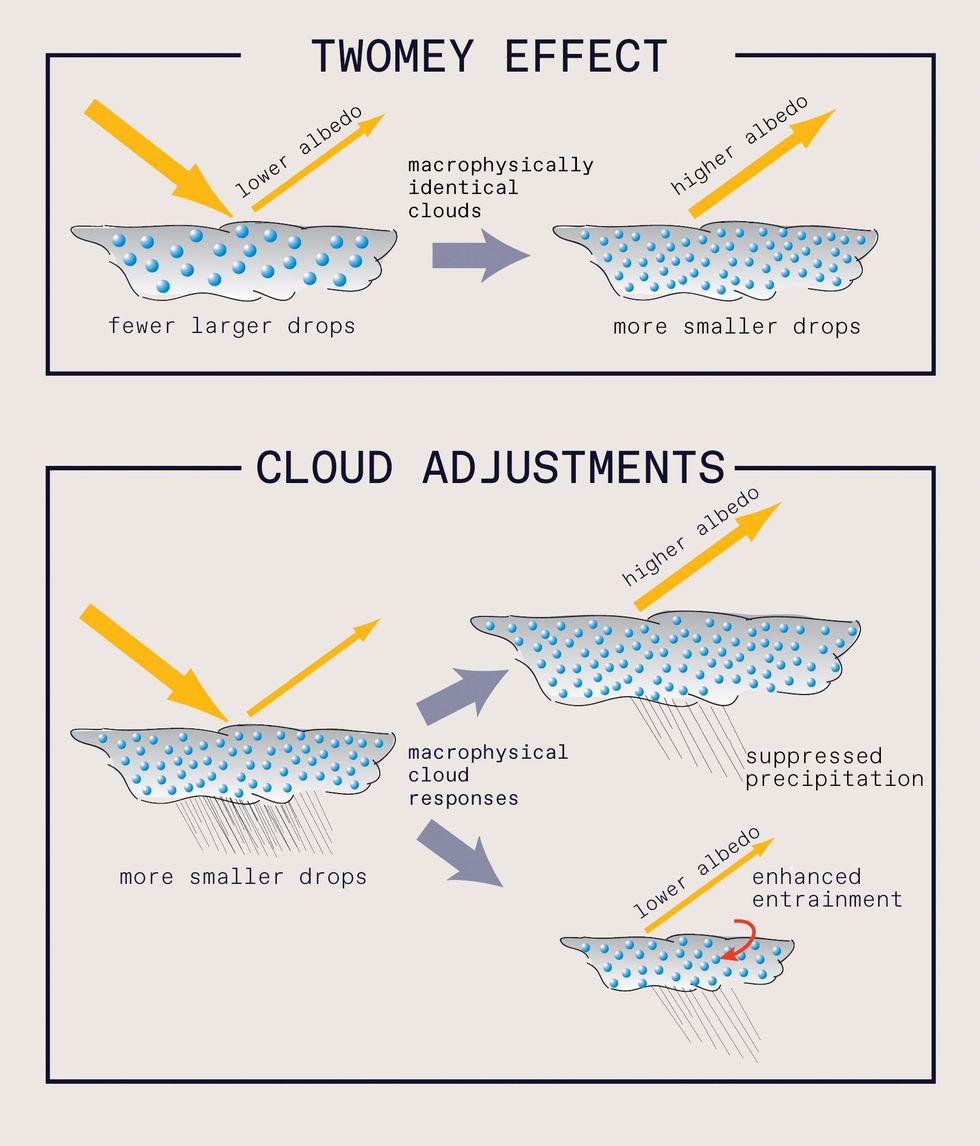
Within the phenomenon referred to as the Twomey impact, clouds with larger concentrations of small particles have the next albedo, that means they’re extra reflective. Such clouds may be much less prone to produce rain, and the retained cloud water would hold albedo excessive. Alternatively, if dry air from above the cloud mixes in (entrainment), the cloud could produce rain and have a decrease albedo. The complete impression of MCB would be the mixture of the Twomey impact and these cloud changes. Rob Wooden
Based mostly on our cloud sort, we will estimate the variety of particles to generate to see a measurable change in albedo. Our calculation entails the standard aerosol concentrations in clear marine stratocumulus clouds and the rise in CCN focus wanted to optimize the cloud brightening impact, which we estimate at 300 to 400 per cubic centimeter. We additionally bear in mind the dynamics of this a part of the environment, referred to as the marine boundary layer, contemplating each the layer’s depth and the roughly three-day lifespan of particles inside it. Given all these components, we estimate {that a} single spray system would want to repeatedly ship roughly 3×10
15 particles per second to a cloud layer that covers about 2,000 sq. kilometers. Because it’s probably that not each particle will attain the clouds, we must always intention for an order or two better.
We will additionally decide the perfect particle dimension primarily based on preliminary cloud modeling research and effectivity concerns. These research point out that the spray system must generate seawater droplets that may dry to salt crystals of simply 30–100 nanometers in diameter. Any smaller than that and the particles is not going to act as CCN. Particles bigger than a pair hundred nanometers are nonetheless efficient, however their bigger mass signifies that power is wasted in creating them. And particles which are considerably bigger than a number of hundred nanometers can have a adverse impact, since they will set off rainfall that leads to cloud loss.
We’d like a transparent understanding of each the efficacy and dangers of photo voltaic local weather intervention applied sciences so folks could make knowledgeable choices about whether or not to implement them.
Creating dry salt crystals of the optimum dimension requires spraying seawater droplets of 120–400 nm in diameter, which is surprisingly tough to do in an energy-efficient method. Typical spray nozzles, the place water is pressured by way of a slender orifice, produce mists with diameters from tens of micrometers to a number of millimeters. To lower the droplet dimension by an element of ten, the stress by way of the nozzle should enhance greater than 2,000 instances. Different atomizers, just like the ultrasonic nebulizers present in residence humidifiers, equally can’t produce sufficiently small droplets with out extraordinarily excessive frequencies and energy necessities.
Fixing this drawback required each out-of-the-box pondering and experience within the manufacturing of small particles. That is the place
Armand Neukermans got here in.
After a distinguished profession at HP and Xerox targeted on manufacturing of toner particles and ink jet printers, in 2009 Neukermans was approached by a number of eminent local weather scientists, who requested him to show his experience towards making seawater droplets. He rapidly assembled a cadre of volunteers—principally retired engineers and scientists. and over the subsequent decade, these self-designated “Previous Salts” tackled the problem. They labored in a borrowed Silicon Valley laboratory, utilizing gear scrounged from their garages or bought out of their very own pockets. They explored a number of methods of manufacturing the specified particle dimension distributions with varied tradeoffs between particle dimension, power effectivity, technical complexity, reliability, and price. In 2019 they moved right into a lab area at PARC, the place they’ve entry to gear, supplies, amenities, and extra scientists with experience in aerosols, fluid dynamics, microfabrication, and electronics.
The three most promising methods recognized by the group had been effervescent spray nozzles, spraying salt water underneath supercritical situations, and electrospraying to type Taylor cones (which we’ll clarify later). The primary possibility was deemed the best to scale up rapidly, so the group moved ahead with it. In an effervescent nozzle, pressurized air and salt water are pumped right into a single channel, the place the air flows by way of the middle and the water swirls across the sides. When the combination exits the nozzle, it produces droplets with sizes starting from tens of nanometers to some micrometers, with the overwhelming variety of particles in our desired dimension vary. Effervescent nozzles are utilized in a variety of functions, together with engines, gasoline generators, and spray coatings.
The important thing to this know-how lies within the compressibility of air. As a gasoline flows by way of a constricted area, its velocity will increase because the ratio of the upstream to downstream pressures will increase. This relationship holds till the gasoline velocity reaches the velocity of sound. Because the compressed air leaves the nozzle at sonic speeds and enters the atmosphere, which is at a lot decrease stress, the air undergoes a speedy radial enlargement that explodes the encompassing ring of water into tiny droplets.
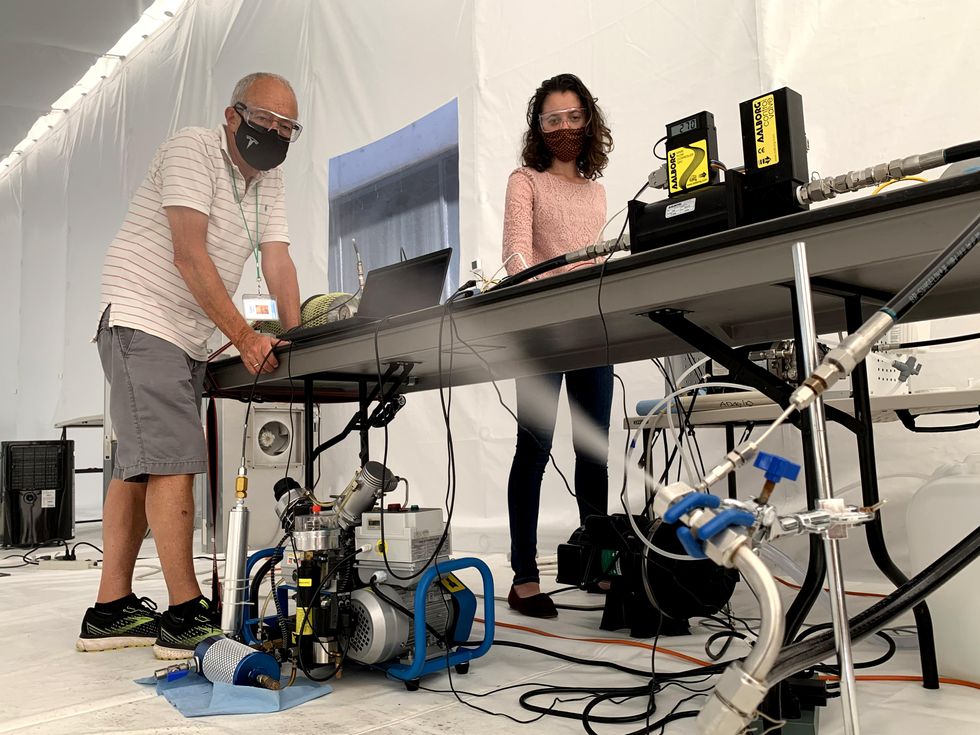

Coauthor Gary Cooper and intern Jessica Medrado take a look at the bubbling nozzle contained in the tent. Kate Murphy
Neukermans and firm discovered that the bubbling nozzle works properly sufficient for small-scale testing, however the effectivity—the power required per accurately sized droplet—nonetheless must be improved. The 2 largest sources of waste in our system are the massive quantities of compressed air wanted and the massive fraction of droplets which are too large. Our newest efforts have targeted on redesigning the movement paths within the nozzle to require smaller volumes of air. We’re additionally working to filter out the massive droplets that might set off rainfall. And to enhance the distribution of droplet dimension, we’re contemplating methods so as to add cost to the droplets; the repulsion between charged droplets would inhibit coalescence, reducing the variety of outsized droplets.
Although we’re making progress with the bubbling nozzle, it by no means hurts to have a backup plan. And so we’re additionally exploring electrospray know-how, which may yield a twig during which virtually 100% of the droplets are inside the desired dimension vary. On this method, seawater is fed by way of an emitter—a slender orifice or capillary—whereas an extractor creates a big electrical subject. If {the electrical} power is of comparable magnitude to the floor stress of the water, the liquid deforms right into a cone, sometimes known as a Taylor cone. Over some threshold voltage, the cone tip emits a jet that rapidly breaks up into extremely charged droplets. The droplets divide till they attain their Rayleigh limit, the purpose the place cost repulsion balances the floor stress. Fortuitously, floor seawater’s typical conductivity (4 Siemens per meter) and floor stress (73 millinewtons per meter) yield droplets in our desired dimension vary. The ultimate droplet dimension may even be tuned by way of the electrical subject right down to tens of nanometers, with a tighter dimension distribution than we get from mechanical nozzles.
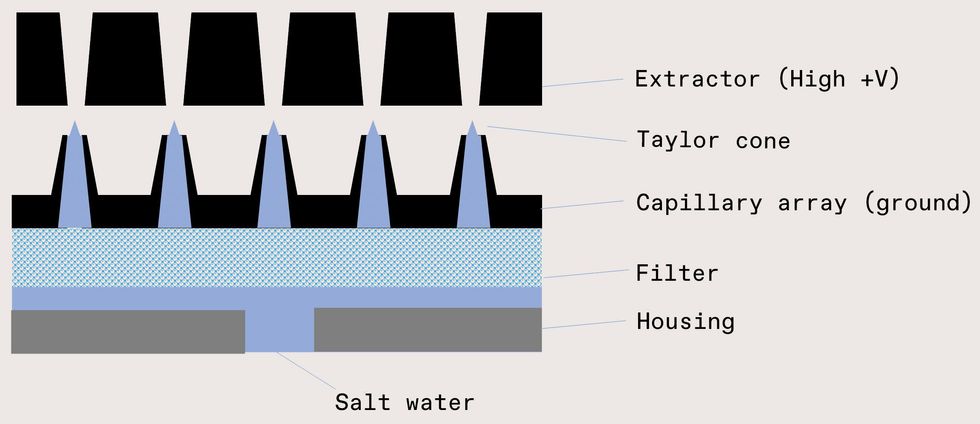
This diagram (to not scale) depicts the electrospray system, which makes use of an electrical subject to create cones of water that break up into tiny droplets. Kate Murphy
Electrospray is comparatively easy to exhibit with a single emitter-extractor pair, however one emitter solely produces 10
7–109 droplets per second, whereas we’d like 1016–1017 per second. Producing that quantity requires an array of as much as 100,000 by 100,000 capillaries. Constructing such an array is not any small feat. We’re counting on methods extra generally related to cloud computing than precise clouds. Utilizing the identical lithography, etch, and deposition methods used to make built-in circuits, we will fabricate massive arrays of tiny capillaries with aligned extractors and exactly positioned electrodes.
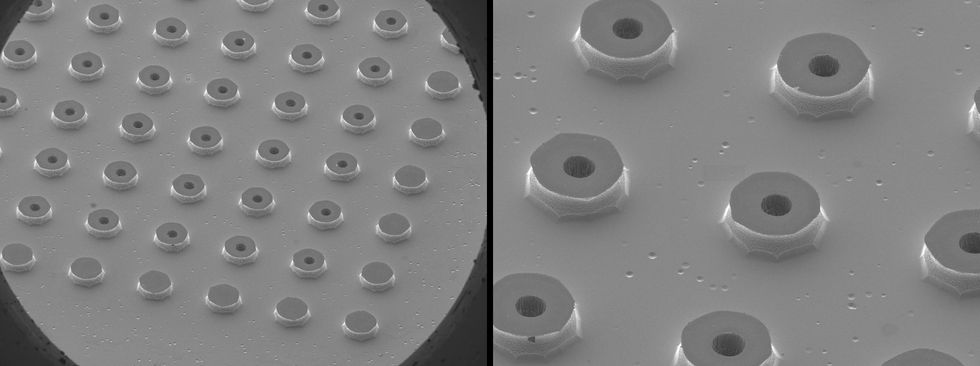
Photos taken by a scanning electron microscope present the capillary emitters used within the electrospray system. Kate Murphy
Testing our applied sciences presents yet one more set of challenges. Ideally, we want to know the preliminary dimension distribution of the saltwater droplets. In follow, that is practically unattainable to measure. Most of our droplets are smaller than the wavelength of sunshine, precluding non-contact measurements primarily based on gentle scattering. As a substitute, we should measure particle sizes downstream, after the plume has advanced. Our main instrument, referred to as a
scanning electrical mobility spectrometer, measures the mobility of charged dry particles in {an electrical} subject to find out their diameter. However that technique is delicate to components just like the room’s dimension and air currents and whether or not the particles collide with objects within the room.
To handle these issues, we constructed a sealed 425 cubic meter tent, outfitted with dehumidifiers, followers, filters, and an array of related sensors. Working within the tent permits us to spray for longer intervals of time and with a number of nozzles, with out the particle focus or humidity turning into larger than what we might see within the subject. We will additionally examine how the spray plumes from a number of nozzles work together and evolve over time. What’s extra, we will extra exactly mimic situations over the ocean and tune parameters comparable to air velocity and humidity.
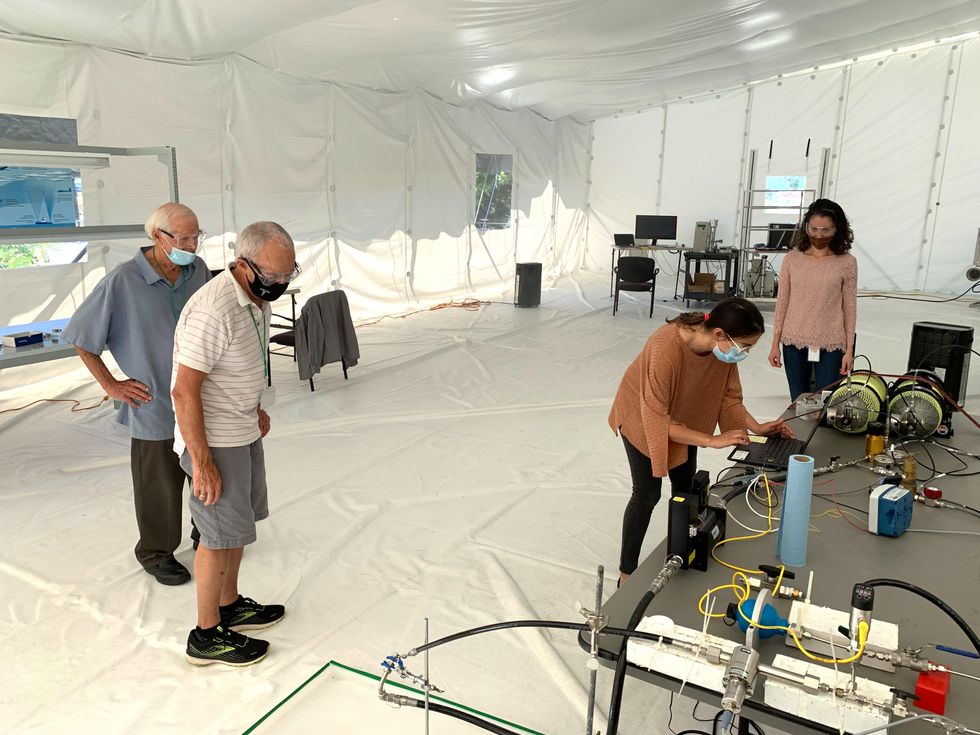

A part of the group contained in the take a look at tent; from left, “Previous Salts” Lee Galbraith and Gary Cooper, Kate Murphy of PARC, and intern Jessica Medrado. Kate Murphy
We’ll ultimately outgrow the tent and have to maneuver to a big indoor area to proceed our testing. The following step shall be outside testing to check plume conduct in actual situations, although not at a excessive sufficient charge that we might measurably perturb the clouds. We would prefer to measure particle dimension and concentrations far downstream of our sprayer, from lots of of meters to a number of kilometers, to find out if the particles raise or sink and the way far they unfold. Such experiments will assist us optimize our know-how, answering such questions as whether or not we have to add warmth to our system to encourage the particles to rise to the cloud layer.
The info obtained in these preliminary exams will even inform our fashions. And if the outcomes of the mannequin research are promising, we will proceed to subject experiments during which clouds are brightened sufficiently to check key processes. As mentioned above, such experiments could be carried out over a small and quick time in order that any results on local weather would not be important. These experiments would supply a vital examine of our simulations, and due to this fact of our capacity to precisely predict the impacts of MCB.
It is nonetheless unclear whether or not MCB may assist society keep away from the worst impacts of local weather change, or whether or not it is too dangerous, or not efficient sufficient to be helpful. At this level, we do not know sufficient to advocate for its implementation, and we’re undoubtedly not suggesting it as an alternative choice to decreasing emissions. The intent of our analysis is to offer policymakers and society with the information wanted to evaluate MCB as one strategy to gradual warming, offering data on each its potential and dangers. To this finish, we have submitted our experimental plans for overview by the
U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and for open publication as a part of a U.S. Nationwide Academy of Sciences examine of analysis within the subject of photo voltaic local weather intervention. We hope that we will make clear the feasibility of MCB as a instrument to make the planet safer.
From Your Web site Articles
Associated Articles Across the Net
[ad_2]
Source
